Authorization
Overview
A combination of roles, permissions, and multi-tenancy provides the framework for authorization and resource isolation.
Roles and Permissions
Cloudify includes built-in user roles with which users are associated:
AdministratorManagerUserOperationsViewer
See the table below to understand the permissions for each role
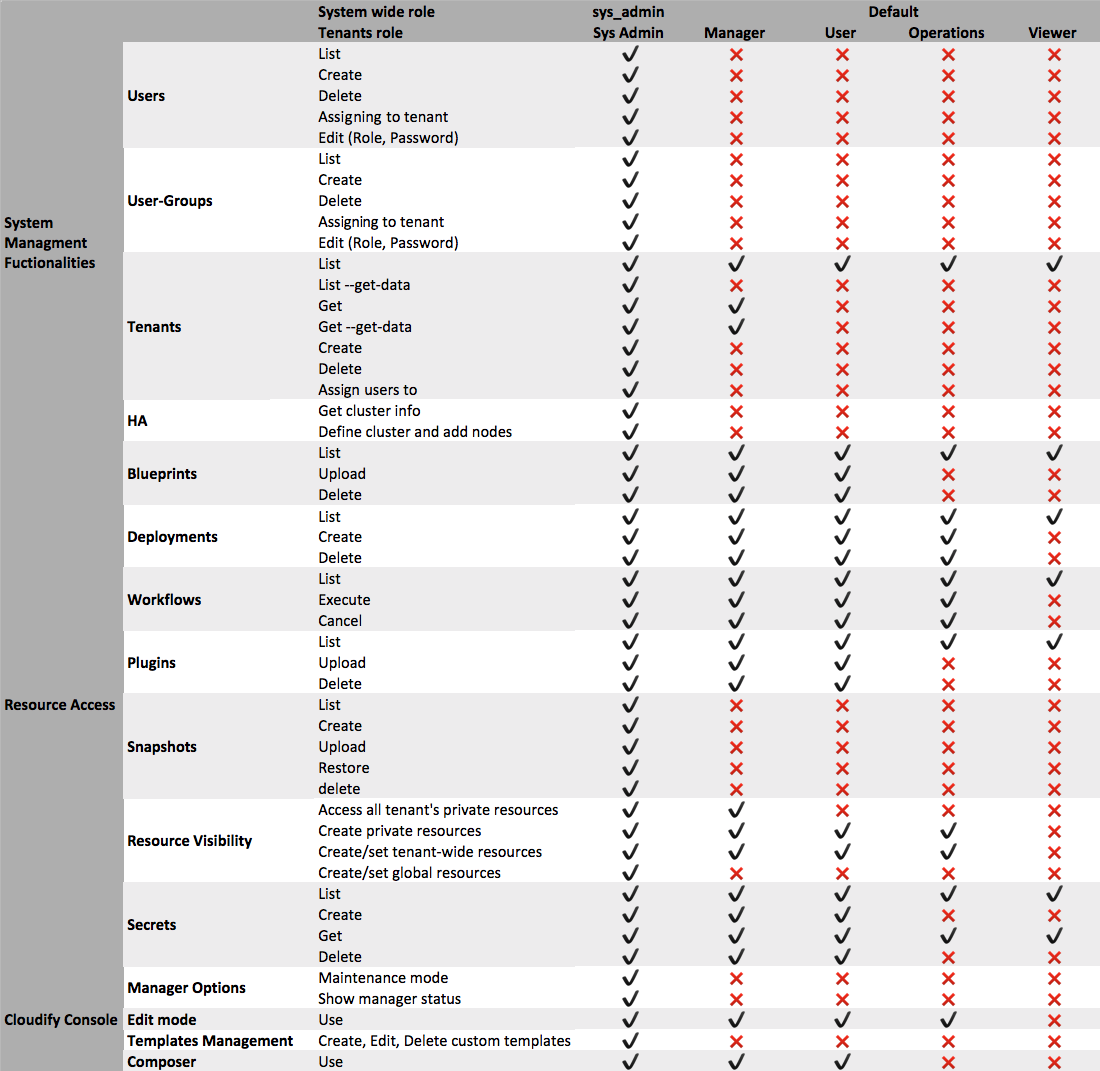
Each role has different permissions, ensuring a role-based access control operation. For example, users with the user role cannot perform Cloudify administration operations such as snapshot management. A user can be suspended using the deactivate command. A deactivated user cannot perform operations.
Isolation
Cloudify supports the concept of users, user groups, and tenants. These elements can be either defined locally in Cloudify or taken from an external user management system (LDAP integration is native). In the latter case, passwords are not stored in Cloudify, authentication is performed via LDAP and a token is generated and used for the user session.
A user can be associated with one or more groups, and one or more tenants.
A group can be associated with one or more tenants.
A user who is authenticated to Cloudify may only access resources that belong to the tenants to which that user has been assigned. Resource isolation is implemented for blueprints, artifacts, deployments, nodes, logs, events, and plugins.
An additional layer of permission control is implemented on resources, allowing private resource configuration. A resource that is created as private is only visible to the user who created that resource, and not to other users within the tenant. The exception is a user with an admin role, who has full access to all system resources.
All REST APIs, except admin APIs and the version API, require a tenant, and operations are associated with the specified tenant. In the case of Read operations, only information about the specified tenant is returned. In the case of Write operations, the resource is added to the specified tenant.
Admin APIs are provided for the following resources (and are available only to admin users):
- Tenant management (CRUD)
- User management (CRUD)
- User group management (CRUD)
- Snapshot management (CRD)
- Cluster management (configuration of manager HA)
- Maintenance mode activation/de-activation
- Upgrade/ rollback commands
RabbitMQ isolation is achieved through the use of virtual hosts and the association between hosts and users, which enables authorization at the queue/ exchange level and results in the isolation of queues between tenants. In this configuration, it is impossible for a host VM from tenant A to access/ request operations on host VMs that belong to tenant B.