Create Blueprint from Terraform module
Getting Started guide to Creating a blueprint from a terraform module deploying and Installing it.
Prerequisites
- Cloudify Manager Version 6.3 or later
- Terraform module archive available from a URL
- Credentials to Cloud provider
Overview
In this guide we are going through following steps to create a blueprint from a terraform module and test it.
- Prepare the manager by defining cloud Credentials Secrets
- Provide a URL to the Terraform archive and chose the right module
- Define the Terraform variables for the Terraform modules
- Define the environment variables for the Terraform module
- Define the outputs and capabilities of the blueprint
- Create a deployment to test the created blueprint
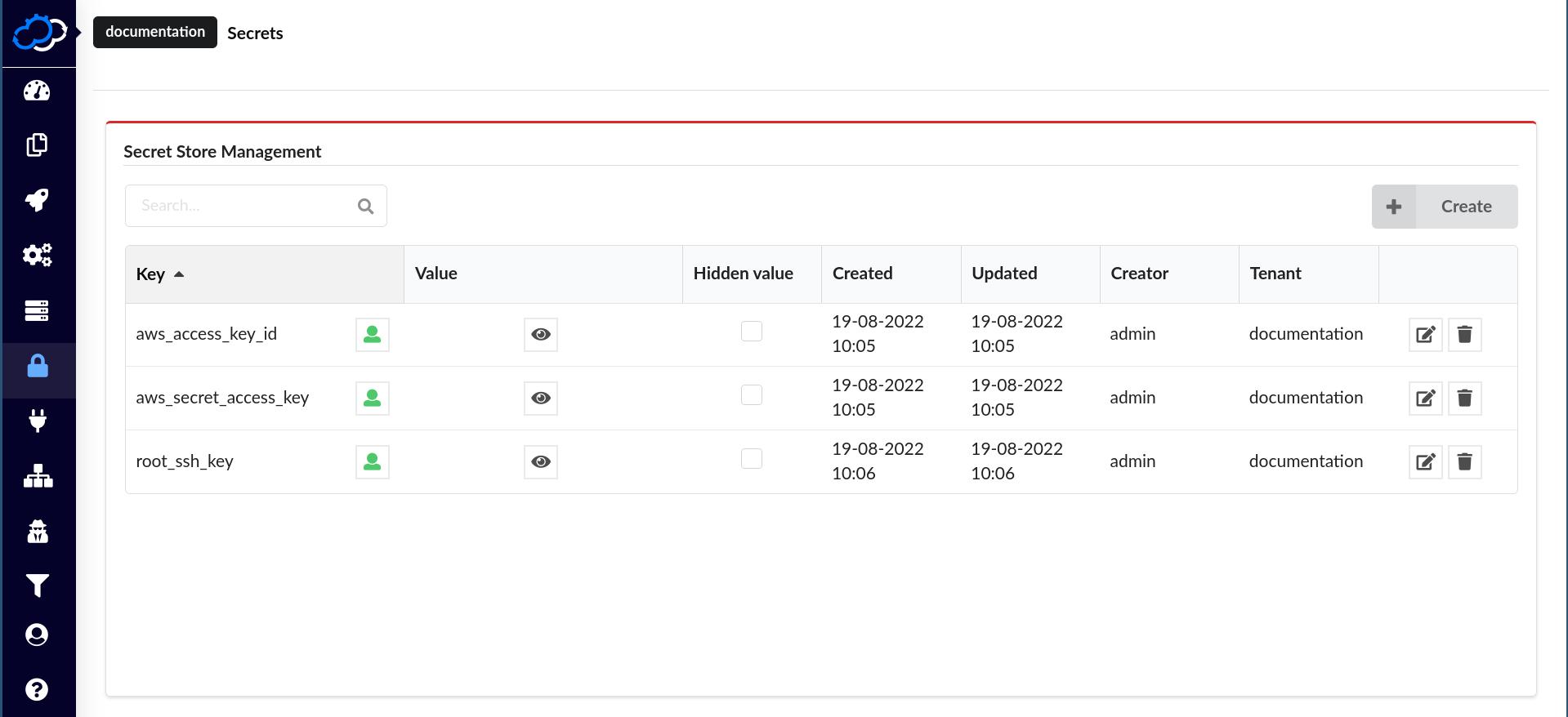
Step 1 Preparation, Define Credentials Secrets
Define secrets for the cloud (cloud credentials you would like to use). The secrets are defined on the secrets page found in the Resources section in the sidebar menu.
In this example we will use an AWS account and setup the following Secrets:
- aws_access_key_id - AWS access key id
- aws_secret_access_key - AWS access key secret
- root_ssh_key - ssh key
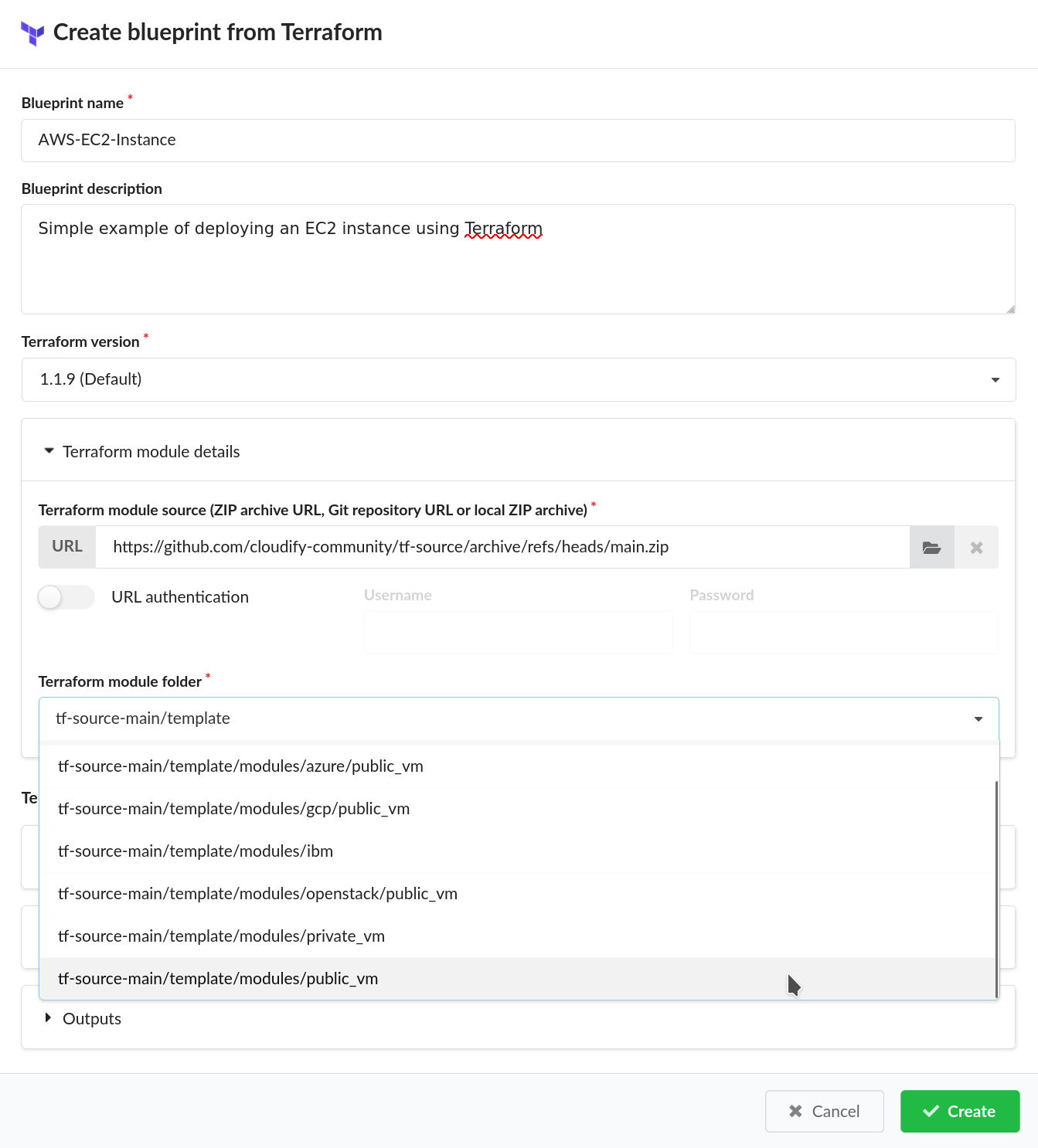
Step 2 Open the Upload Dialog and define the blueprint name.
Go to the Blueprints page and from the Upload dropdown select the “Upload from Terraform module”. You should see the Create blueprint from the Terraform dialog.
- Type in that dialog the name for the blueprint.
- Select the Terraform version that you would like to use.
Step 3 Provide a URL to the Terraform archive and choose the module.
Provide a URL to the archive containing the Terraform module.
- The folder structure of the archive should start with a single root folder, This root folder can contain the Terraform module, or subfolders with multiple modules.
- It’s possible to use archive URL’s that are generated by services like Github (as we do in this example). Select the path to the Terraform module
- For archives that contain multiple modules, you are able to choose the module you need by selecting the path in the dropdown.
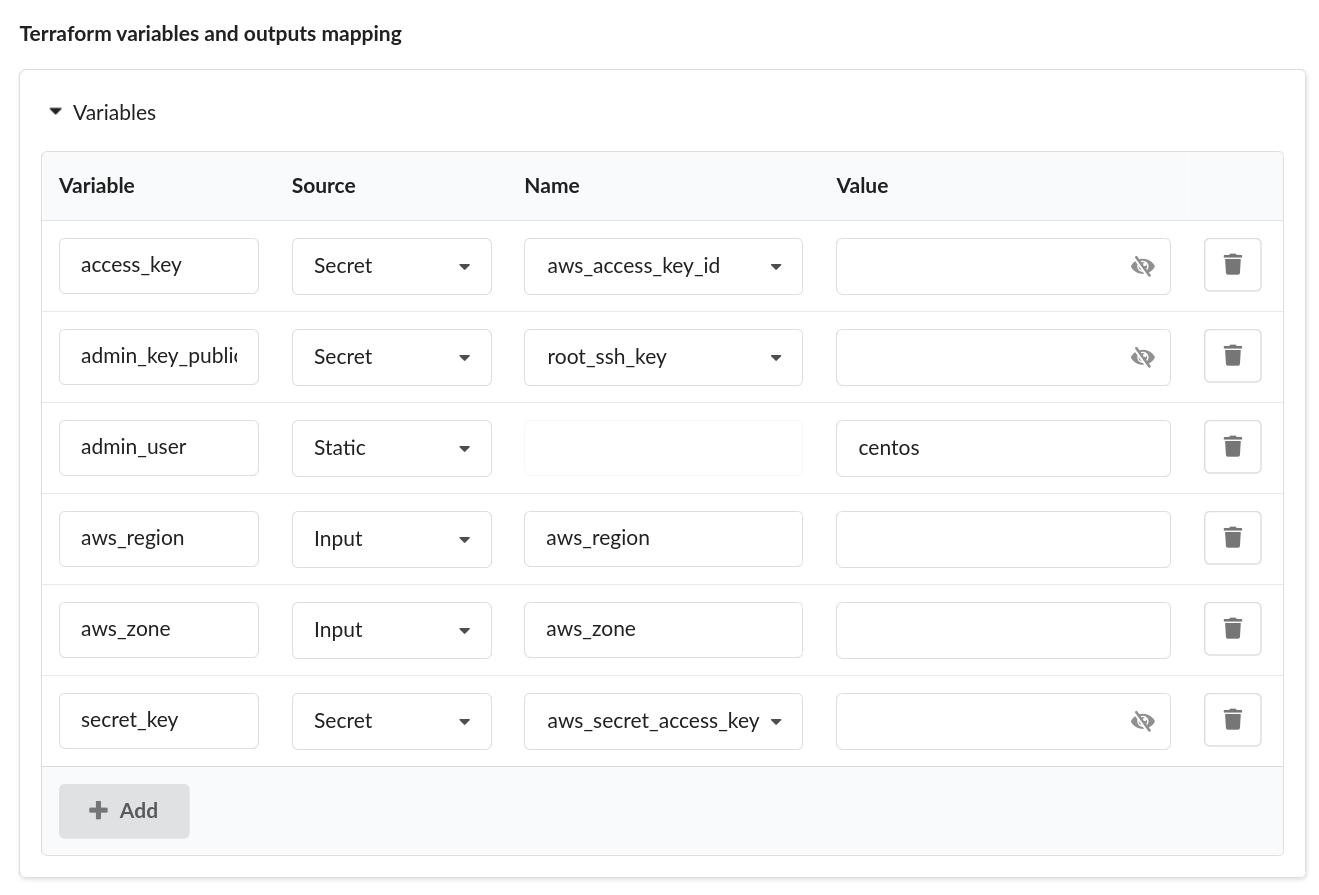
Step 4 Define the variables for the Terraform module
- Open the variables section and click the ‘Add’ button
- Type the variable name
- Select the source type and a value / input name / secret name
- Static value - A Value that will always be assigned to the variable
- Input - the variable that will be set by an input that will be presented when a deployment is created.
- Secret - The value assigned to the variable that will be taken from the secret store.
If the Terraform module dose not have credentials set as variables, see below title “Using modules from Registry, Passing provider credentials by defining the Environment Variables” In our example we will map the variables to the secrets with the account AWS credentials
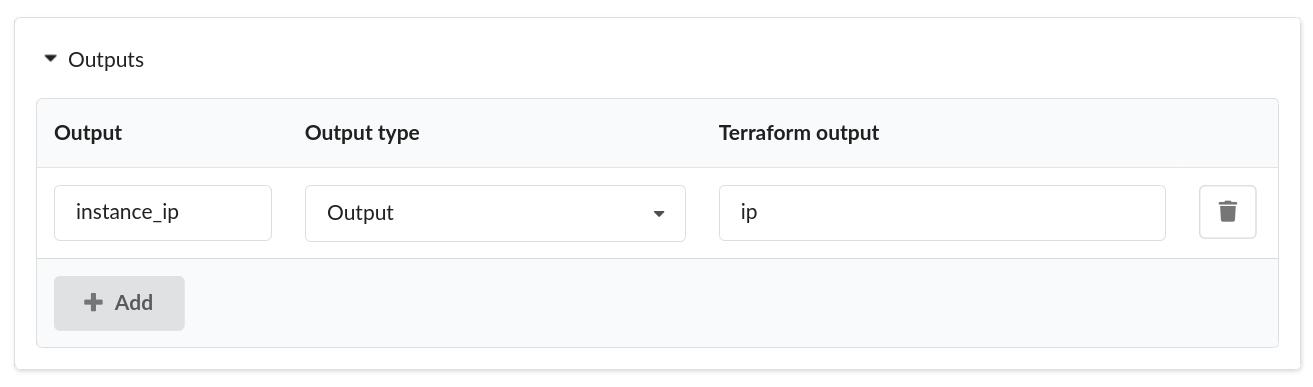
Step 5 Define the outputs and capabilities of the blueprint
The outputs of the Terraform module can be made available in the outputs and capabilities in Cloudify.
When to use output and when to use a capability:
- Define outputs to display information to the user or export to other system
- Define capabilities for information you would like to make available for other deployments and service composition.
Step 6 Create the blueprint
Submit the dialog, errors discovered will appear in the dialog. After successful submission you will be forwarded to the blueprint page.
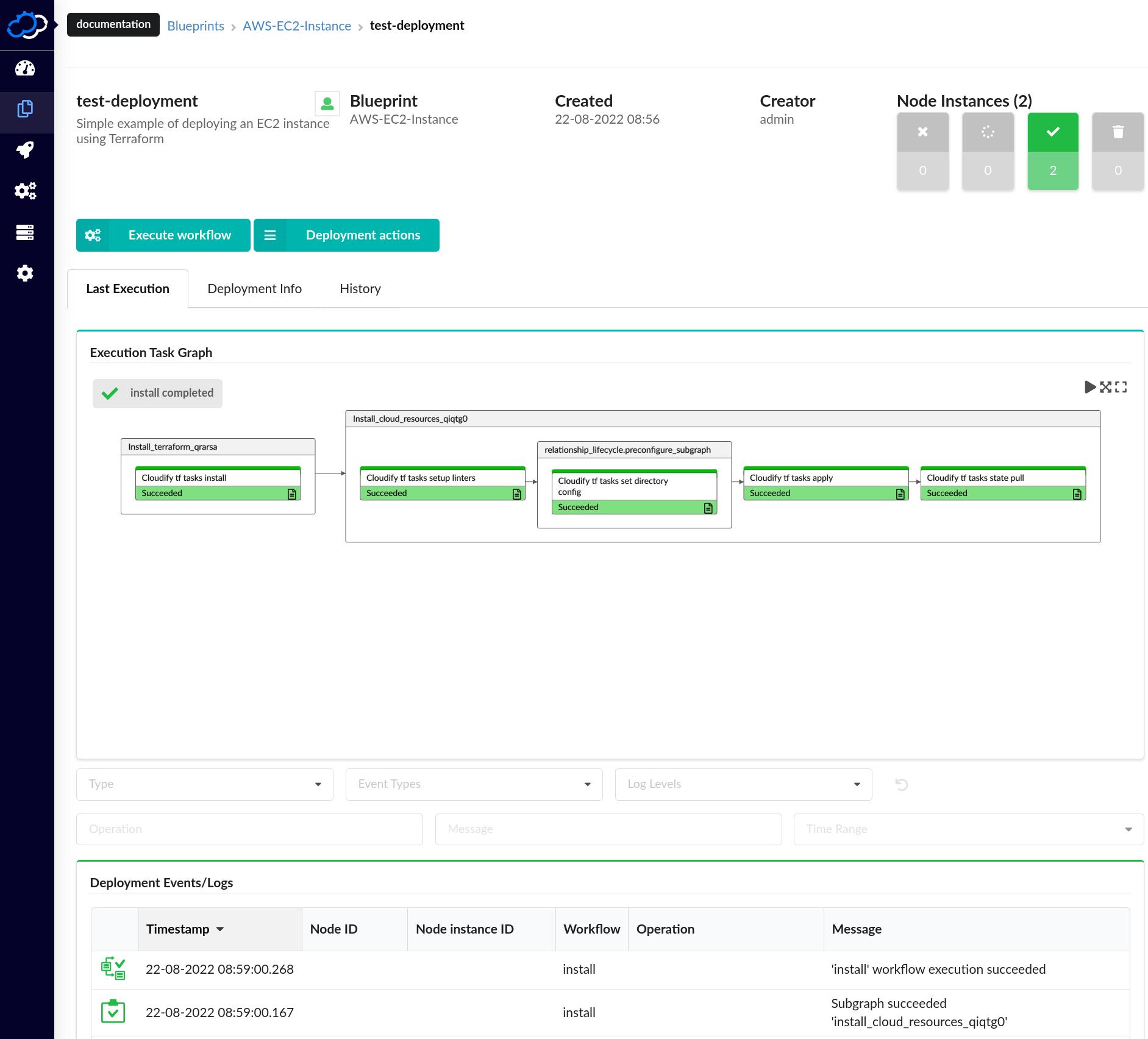
Step 7 Create a Deployment and Test the blueprint
- Click the ‘create deployment’ button.
- Review the logs, located in the logs section of the deployment page
- Review deployment output
- Review the inputs in the Deployment Creation dialog
- Inspect the install workflow execution graph until it will finished, The bars of the execution graph will turn green when operations will finish.
- Review the logs section of the deployment’s page
- Click the Deployment info tab and review the outputs section, There you will find the outputs of the terraform module defined in the blueprint
Using modules from Registry, Passing provider credentials by defining the Environment Variables
Some Terraform modules, like those downloaded from the registry, rely on environment variables to supply credentials and other information to the providers needed. You can define the environment variable and assign it with values in the ‘environment variables’ section - as per configured in the variable section. The current blueprint we are creating gets credentials from the variables, while we examine an example Environment Variables section: AWS Example:
- Environment Variable: AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID Type: Secret Secret’s Name: aws_access_key_id
- Environment Variable: AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY Type: Secret Secret’s Name: aws_secret_access_key
- Environment Variable: AWS_DEFAULT_REGION Type: static Value: us-west-2
Troubleshooting
- The credentials were defined in the variables section instead of the environment variables section
- Error: Value for undeclared variableThe root module does not declare a variable named “AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID” but a value was found in…
- The Version of terraform selected was too old for the terraform module you have uploaded.
- Error: Could not load pluginPlugin reinitialization required. Please run “terraform init”.
- Credentials were not defined.
- Error: configuring Terraform AWS Provider: no valid credential sources for Terraform AWS Provider found.
