Multiple Instances (Scaling)
This section describes the different concepts involved in scaling components of your application blueprint.
Multiple instances and scaling, refers to the number of node instances each node template will have on deployment,
and changes made to that number during run-time after the deployment is created, using the scale workflow.
There are two ways of specifying this configuration in an application blueprint. The first relates to configuring the number of node instances on a per-node template basis, using the scalable capability configuration. The second method primarliy relates to configuring the number of node instances on a group basis, in which the group contains several node templates.
These concepts are described in the following explanations and examples, including the difference between these two methods, and how the number of instances for different nodes may be changed during runtime.
Node Templates scalable Configuration
To specify the initial number of instances a node template will have, the node template capabilities.scalable properties must be configured.
For example, to configure a VM node template so that it will be deployed with fivew initial instances, the following configuration can be used:
node_templates:
example_vm:
type: cloudify.nodes.Compute
capabilities:
scalable:
properties:
default_instances: 5See Node Templates for additional details.
Scaling Policy and Scaling Groups Configuration
To specify the initial number of instances a group of node templates will have as a single unit, use scaling policies and groups.
For example, to configure a scaling group for a VM and an IP, the following configuration can be used:
node_templates:
vm:
type: cloudify.nodes.Compute
ip:
type: cloudify.nodes.VirtualIP
groups:
vm_and_ip:
members: [vm, ip]
policies:
scale_policy1:
type: cloudify.policies.scaling
properties:
default_instances: 5
targets: [vm_and_ip]When deployed, five vm node instances and five ip node instances will be created.
See Policies for additional details.
Combining Node Template scalable With Scaling Groups
A node template can have have its scalable capability configured and can also be included in a scaling group. For example:
node_templates:
vm:
type: cloudify.nodes.Compute
capabilities:
scalable:
properties:
default_instances: 3
groups:
vm_group:
members: [vm]
policies:
scale_policy1:
type: cloudify.policies.scaling
properties:
default_instances: 5
targets: [vm_group]When deployed, 15 (3 * 5) vm node instances are created.
-
You can nest scaling groups, meaning that a scaling group can have another scaling group as one of its members.
-
Between members of the same scaling group, using the
get_attributeintrinsic function in the blueprint, with explicit reference to a node by its name (i.e. notSELF,SOURCEorTARGET) can be used in places where otherwise, an ambiguity would exist. Seeget_attributeintrinsic function for additional details.
connected_to/depends_on Relationship Semantics
This section describes how connected_to/depends_on relationships behave between node instances that belong to the same scaling group instance.
Generally, when two node templates are related via a connected_to/depends_on relationship, relationship instances exist from all node instances of the source node to all node instances of the target node. For more information, see the all_to_all example.
Similar logic applies between node templates that belong to the same scaling group. The exception is that the relationship instances between the node instances do not “escape” scaling group boundaries, as shown in the following example.
node_templates:
application:
type: web_app
capabilities:
scalable:
properties:
default_instances: 2
relationships:
- type: cloudify.relationships.connected_to
target: database
database:
type: database
capabilities:
scalable:
properties:
default_instances: 2
groups:
application_and_database:
members: [application, database]
policies:
scale_policy2:
type: cloudify.policies.scaling
properties:
default_instances: 2
targets: [application_and_database]When the above blueprint snippet is deployed, there are two instances of the application_and_database scaling group. Each scaling group contains two node instances of the application node and two node instances of the database node.
The following diagram shows how the different node instances are connected. Specifically, shows how connected_to relationships do not “escape” scaling group boundaries.
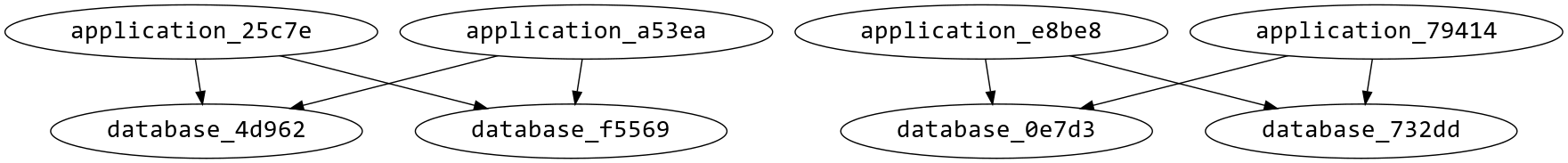
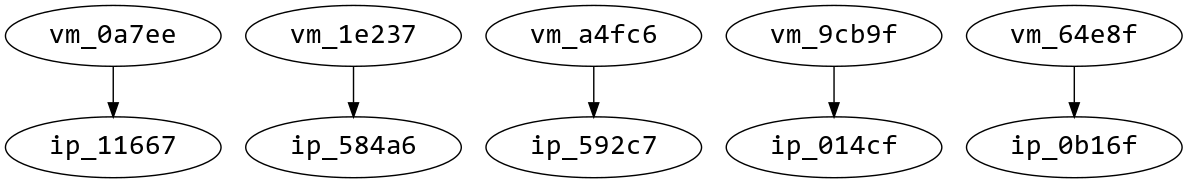
The following diagram builds upon the blueprint previously provided, in which there are five vm_and_ip scaling group instances with a vm and ip node instance in each scaling group instance.
If the vm node was to have a connected_to relationship to the ip node, the relationships would behave as shown in the diagram.
contained_in Relationship Semantics
Implicit Scaling Group Membership
If node A is contained_in node B and node B is part of scaling group S, then node A is also implicitly included in S.
For example, in the following example in which a db node template is contained_in a vm node template, both group definitions are equivalent:
node_templates:
vm:
type: cloudify.nodes.Compute
db:
type: cloudify.nodes.DBMS
relationships:
- target: vm
type: cloudify.relationships.contained_in
groups:
vm_group:
members: [vm, db]
# is equivalent to
vm_group:
members: [vm]
policies:
scale_policy1:
type: cloudify.policies.scaling
targets: [vm_grop]Scaling groups and contained_in Semantics.
The semantics for contained_in relationships are described in detail here.
Building on those semantics, the following example describes how a scaling group fits in.
node_templates:
vm:
type: cloudify.nodes.Compute
capabilities:
scalable:
properties:
default_instances: 2
app:
type: web_app
relationships:
- type: cloudify.relationships.contained_in
target: vm
db:
type: database
relationships:
- type: cloudify.relationships.contained_in
target: vm
groups:
app_and_db:
members: [app, db]
policies:
scale_policy2:
type: cloudify.policies.scaling
properties:
default_instances: 2
targets: [app_and_db]Deploying the previous blueprint produces the following topology.

You can see in the diagram that two vm node instances are deployed, as expected from the blueprint definition.
Each vm node instance has two db and two app node instances contained in it. In other words, each vm node instance “contains” two instances of the app_and_db scaling group, as defined in the blueprint.
This shows that scaling groups can be “contained in” node templates when their members are contained_in some other node templates.
Scale Workflow
To change the number of node instances during run-time (i.e. after the deployment is installed), use the scale workflow.
See Scale Workflow for additional details.
