Overview of Open Source Components in Cloudify
This section is to provide information about how the Cloudify architecture supports currently-implemented flows. Operational knowledge is assumed.
Cloudify Manager primarily is built with open-source components. The relationships between the components in the Cloudify Manager architecture is illustrated in the diagram below.
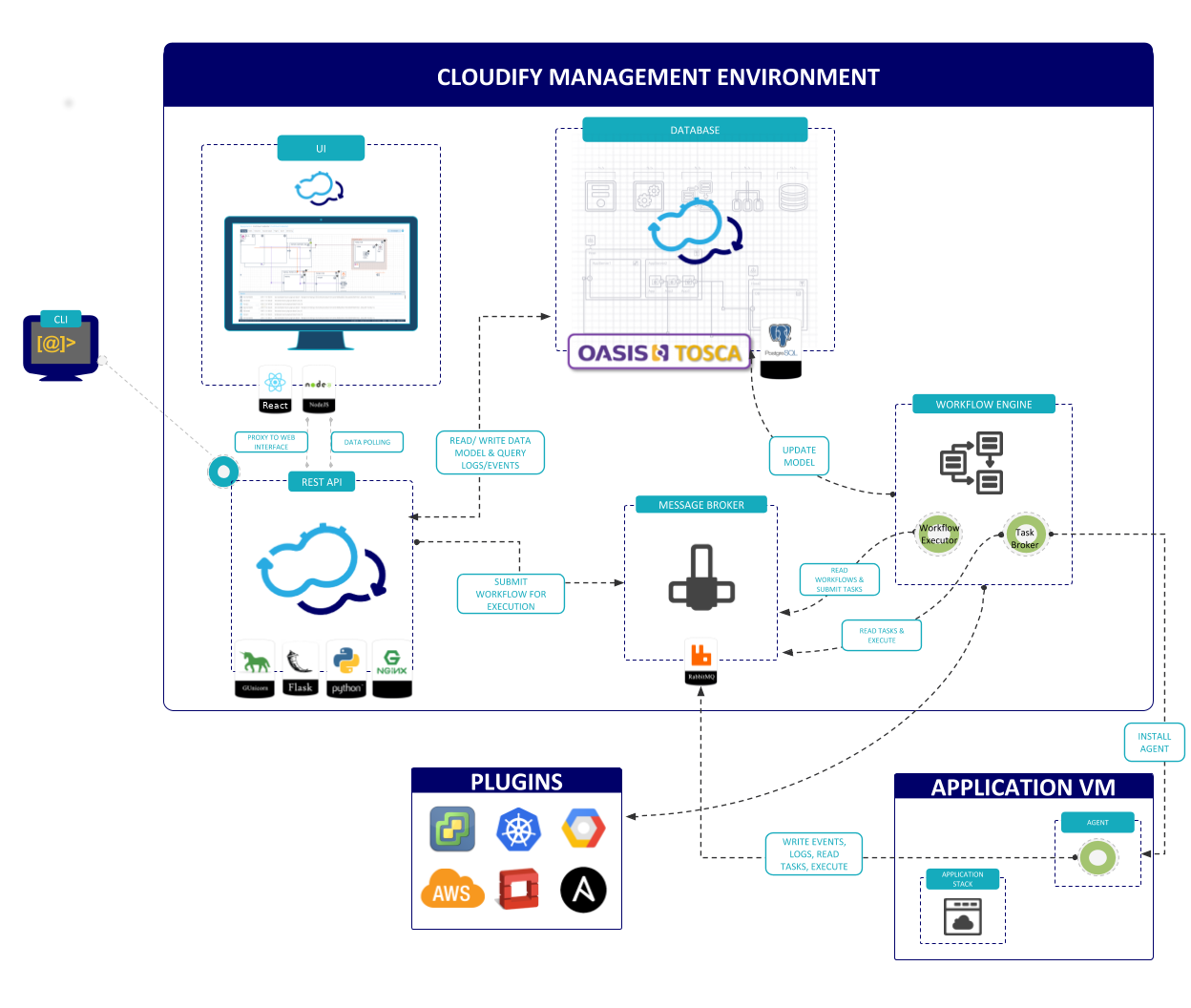
Ports and Entry Points
Rather than specifying the ports in each component’s overview, ports are specified here so that you can easily review network requirements.
External Ports
All ports are TCP ports unless stated otherwise
By default, there are two external networks from which the Cloudify management environment is accessed:
- The network on which the CLI resides, which is potentially a user’s
management network. - The network on which the application resides, which is potentially a user’s application network.
Therefore, Cloudify requires only two entry points to its management environment:
- Ports 80 / 443 for user rest-service/UI access via Nginx
- Port 22 is exposed for SSH access, to enable remote access to the Cloudify management environment.
This is required for the
cfy sshcommand to work.
Application Ports
The following ports are exposed for agent-manager communication:
- The REST service and the fileserver are accessed via port 53333
- RabbitMQ is accessed via port 5671
The agents use the REST service to update the application’s model (for example, setting runtime-properties). Agents connect to RabbitMQ to receive tasks.
Local ports
The following additional ports are exposed on localhost, and used by the manager internally:
- RabbitMQ uses port 15671 for the management API access
- The UI backend uses port 8088
- PostgreSQL uses port 5432 for database access
- InfluxDB uses port 8086 for HTTP API access
- Logstash uses a dummy port 9999 to verify the communication is live
High Availability Ports
The following additional ports are used for communication between nodes in a Cloudify Manager cluster:
- Consul is using TCP and UDP ports 8300 and 8301
- Consul exposes port 8500 for HTTPS API access
- PostgreSQL exposes port 15432 for database replication
- Syncthing exposes port 22000 for filesystem replication
Nginx
Nginx is a high-performing Web server. In Cloudify Manager, it serves two purposes:
- A proxy for the Cloudify REST service and Cloudify Console
- A file server to host Cloudify-specific resources, agent packages and blueprint resources.
File Server
The file server served by Nginx, is available at https://{manager_ip}:53333/resources, which is mapped to the /opt/manager/resources/ directory. You must authenticate in order to access the file server.
To access subdirectories that include tenant names in their path, you must have privileges on that tenant. These subdirectories are:
blueprintsuploaded-blueprintsdeploymentstenant-resources
The directories that are stored in snapshots are:
blueprintsuploaded-blueprintsdeploymentstenant-resourcespluginsglobal-resources
The tenant-resources and global-resources directories are not used by Cloudify Manager and can be created by the user for storing custom resources.
Gunicorn and Flask
Gunicorn is a Web server gateway interface HTTP server. Flask is a Web framework.
Together, Gunicorn and Flask provide the Cloudify REST service. The REST service is written using Flask, and Gunicorn is the server. Nginx, is the proxy to that server. The Cloudify’s REST service is the integrator of all parts of the the Cloudify environment.
PostgreSQL
PostgreSQL is an object-relational database that can handle workloads ranging from small single-machine applications to large Internet-facing applications.
In Cloudify Manager, PostgreSQL serves two purposes:
- Provides the main database that stores the application’s model (i.e. blueprints, deployments, runtime properties)
- Provides indexing, and logs’ and events’ storage
Logstash
Logstash is a data handler. It can push/pull messages using several inputs, and apply filters and output to different outputs.
Logstash is used by Cloudify to pull log and event messages from RabbitMQ and index them in PostGresSQL.
RabbitMQ
RabbitMQ is a queue-based messaging platform.
RabbitMQ is used by Cloudify as a message queue for different purposes:
- Queueing deployment tasks
- Queueing logs and events
- Queueing metrics
Riemann
Riemann is an event stream processor used primarily for monitoring.
Riemann is used within Cloudify as a policy-based decision maker. For more information on policies, see the policies section.
The use of Riemann as a policy engine in Cloudify is an experimental feature and, as such, is not guaranteed to be forward-compatible.
Pika
Pika is a pure-Python implementation of the AMQP 0-9-1 protocol.
The Cloudify management worker and the host agents are using pika to
communicate with RabbitMQ.
Management Worker (or Agent)
Both the Workflow Executor and the Task Broker that appear in the diagram are part of the Cloudify Management Worker.
- The
Workflow Executorreceives workflow execution requests, creates the tasks specified by the workflow, submits the tasks for execution by host agents and theTask Broker, and manages workflow state. - The
Task Brokerexecutes API calls to IaaS providers to create deployment resources, and executes other tasks specified incentral_deployment_agentplugins.
Note that all agents (the Management Worker, and agents deployed on application hosts) are using the same implementation.
InfluxDB
InfluxDB is a time-series database.
- A proprietary metrics consumer is used to pull metrics from RabbitMQ and submit them to InfluxDB.
- InfluxDB is used by Cloudify to store metrics that are primarily submitted by the application’s hosts.
