Creating a Deployment
Get the latest docs
You are looking at documentation for an older release. Not what you want? Go to the current release documentation.In order for Cloudify to deploy your application, it reads the uploaded blueprint YAML (the logical representation) and manifests a model called a deployment. A deployment is a “technical” drilled-down representation of your application. For example, if a blueprint describes a single server node that is defined to deploy multiple instances, the deployment will comprise the instances themselves, together with their unique identifiers.
Creating a deployment does not actually create any resources, it simply generates a “physical” representation of your application from a “logical” (blueprint) representation and stores it in the database. Technically, it is a virtual environment on Cloudify Manager.
Creating a Deployment via the CLI
To create a deployment using the Cloudify CLI execute:
cfy deployments create -b <BLUEPRINT_NAME> <DEPLOYMENT_NAME> --inputs </path/to/your/inputs.yaml>
Creating a Deployment via the Cloudify Web UI
On the Blueprints widget, select the required blueprint and click Deploy.
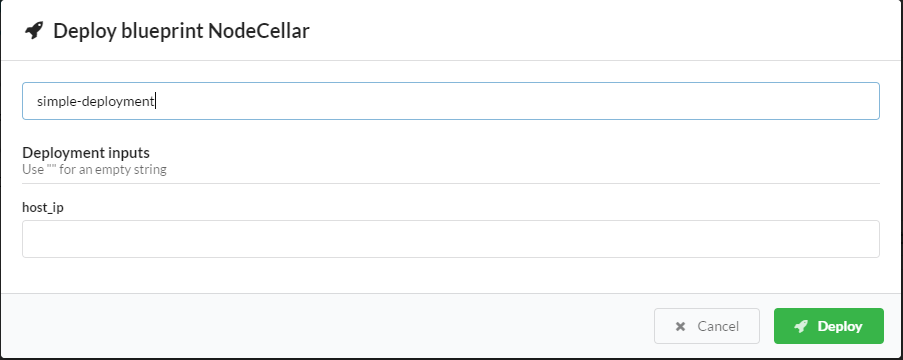
Enter the name of the deployment and, optionally, specify the raw input parameters.
Click Deploy.
After creating the deployment, you can open the Deployment widget to track the initialization stage.
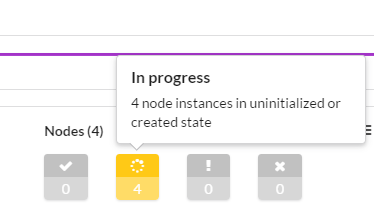
For information about deployment states, see the Deployments Page documentation.
After initialization is complete, you can start using the deployment and executing workflows.
Example: Creating a Deployment
This example shows how a deployment can be created for a blueprint, using the command line. For more information about creating deployments using the command line, click here.
First create an inputs file (in a similar way to the Manager blueprint’s inputs dialog):
inputs:
image:
description: >
Image to be used when launching agent VM's
flavor:
description: >
Flavor of the agent VM's
agent_user:
description: >
User for connecting to agent VM's
Make a copy of the inputs template already provided and edit it:
cd cloudify-nodecellar-example/inputs/openstack.yaml.template
cp openstack.yaml.template inputs.yaml
The inputs.yaml file should look somewhat like this:
image: 8c096c29-a666-4b82-99c4-c77dc70cfb40
flavor: 102
agent_user: ubuntu
All inputs have default values so no input file is needed.
To specify different values for one or more inputs, create an inputs.yaml file with the required inputs, for example:
echo -e "domain: 'my_domain.org'\nlocation: '168642'" > inputs.yaml
The inputs.yaml file will look like this:
domain: 'my_domain.org'
location: '168642'
inputs:
image:
description: >
Image to be used when launching agent VM's
flavor:
description: >
Flavor of the agent VM's
agent_user:
description: >
User for connecting to agent VM's
Make a copy of the inputs template already provided and edit it:
cd cloudify-nodecellar-example/inputs
cp aws-ec2.yaml.template inputs.yaml
The inputs.yaml file should look somewhat like this:
image: ''
size: ''
agent_user: ''
The image is again the AMI image ID. The size is the instance_type, and the agent user is the default user agent on the image type.
inputs:
vcloud_username:
type: string
vcloud_password:
type: string
vcloud_url:
type: string
vcloud_service:
type: string
vcloud_vcd:
type: string
catalog:
type: string
template:
type: string
agent_user:
type: string
default: ubuntu
management_network_name:
type: string
floating_ip_gateway:
type: string
nodecellar_public_ip:
type: string
Make a copy of the inputs template already provided and edit it:
cd cloudify-nodecellar-example/inputs
cp vcloud.yaml.template inputs.yaml
The inputs.yaml file should look somewhat like this:
{
"vcloud_username": "your_vcloud_username",
"vcloud_password": "your_vcloud_password",
"vcloud_url": "https://vchs.vmware.com",
"vcloud_service": "service_name",
"vcloud_vdc": "virtual_datacenter_name",
"manager_server_name": "your_manager",
"manager_server_catalog": "templates_catalog",
"manager_server_template": "template",
"edge_gateway": "gateway_name",
"floating_ip_public_ip": "",
"management_network_name": "management",
"manager_private_key_path": "~/.ssh/vcloud_template.pem",
"agent_private_key_path": "~/.ssh/vcloud_template.pem"
}
